Abscesses (Boils)
What are Abscesses (Boils)?
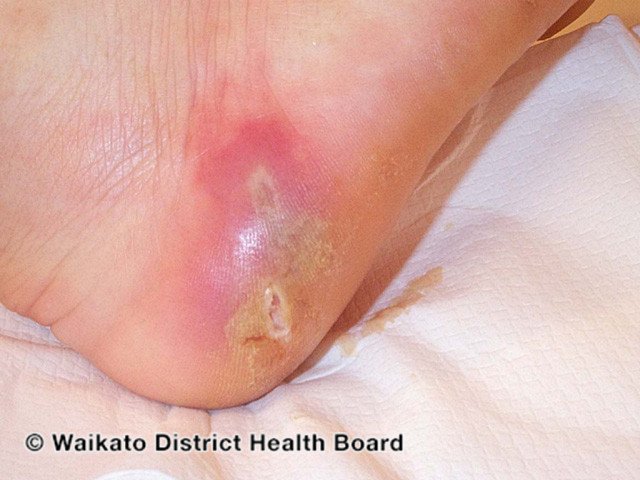
Abscesses, commonly known as boils, are painful, pus-filled lumps that form under the skin when bacteria infect a hair follicle or oil gland. They can appear anywhere on the body, but most frequently develop on areas prone to friction or hair, such as the face, neck, armpits, groin, and buttocks.
What causes Abscesses (Boils)?
The primary cause of an abscess is bacterial infection, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus. Factors contributing to the development of abscesses include:
Breaks in the skin, such as cuts or insect bites
Folliculitis or In-grown hairs
Blocked sweat glands or oil ducts
Weak immune system, making one more susceptible to infections
Chronic skin conditions like acne, eczema, or hidradenitis
What are the symptoms of Abscesses (Boils)?
Typically, an abscess starts as a red, tender bump. Over time, it becomes larger, more painful, and may turn white as pus accumulates beneath the skin. Symptoms include:
Swelling and redness around the lump
Increase in size, sometimes rapidly
Pain, warmth, and tenderness in the affected area
Yellow or white center, from which pus might drain
Fever or chills (indicative of a more severe infection)
How do I treat Abscesses (Boils)?
While some abscesses resolve on their own, others might require medical intervention:
Warm Compress: Applying a warm, wet cloth can help drain the abscess naturally.
Antibiotics: If bacteria cause the infection, a doctor might prescribe oral antibiotics.
Incision and Drainage: In some cases, a healthcare provider might make a small cut in the abscess to drain the pus.
Avoid Squeezing: It's essential not to try to puncture or squeeze the abscess, as it can push the infection deeper or spread it to surrounding tissues.
How do I prevent Abscesses (Boils)?
To reduce the risk of developing abscesses:
Hygiene: Regularly wash with mild soap, and ensure cuts or scrapes are kept clean and dry. If you get abscesses regularly, we may recommend an antibacterial soap to use to help with prevention.
Avoid Tight Clothing: Tight clothing can cause friction, leading to ingrown hairs or skin irritation.
Maintain Immune Health: Ensure a balanced diet, adequate sleep, and manage stress to bolster the immune system.
Be Aware of Personal Items: Avoid sharing personal items like razors or towels, which can harbor bacteria.
An skin abscess as a result of an injection, with surrounding erythema.
Credit: DermNet NZ
An abscess in the armpit which can be seen in the setting of hidradenitis suppurativa.
Credit: DermNet NZ


