Merkel Cell Carcinoma
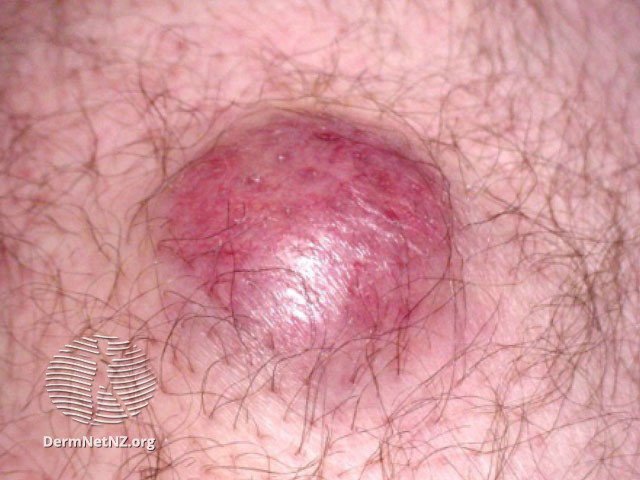
Merkle cell carcinoma is an aggressive skin cancer that can often resemble basal cell carcinoma.
Credit: DermNet NZ
What is Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare, yet aggressive type of skin cancer. It typically appears as a firm, painless lump that varies in color from flesh-toned to red. Though frequently found on the head or neck, it can manifest anywhere on the body and has the potential to spread or metastasize.
What causes Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
The majority of Merkel cell carcinomas tested are linked to the Merkel cell polyomavirus. This virus is believed to induce cellular mutations, resulting in rapid cell growth. Factors elevating the risk of developing this carcinoma include excessive UV light or sun exposure and immunosuppression. While initially thought to originate from Merkel cells, specialized pressure receptors in the skin, the true cellular origin remains a subject of debate.
What are the symptoms of Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
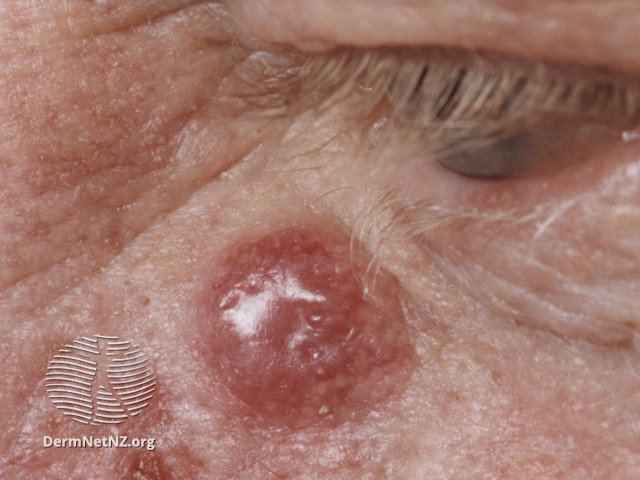
Merkel cell carcinomas generally manifest as flesh-colored, red, or blue tumors that can range from 0.5 to 5 cm in size and display swift enlargement. These tumors can emerge anywhere on the body, but roughly half of them appear on the head and neck, followed by the arms and legs. It predominantly affects older individuals. Its appearance often resembles other prevalent skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma, but it demonstrates a faster growth rate. If the cancer has metastasized, additional lumps may be detected in the groin, armpits, or neck.
How do I treat Merkel Cell Carcinoma?
The primary treatment method for Merkel cell carcinoma is a comprehensive excision of the tumor and its surrounding area, especially if detected early. In many instances, it's also recommended to remove adjacent lymph nodes. Subsequent radiation treatment is commonly employed to minimize the risk of further progression. In more severe cases where the carcinoma has advanced, chemotherapy may be administered. Given its aggressive nature, early detection and intervention are paramount.
Merkel cell carcinoma can look like a rapidly growing pink or purple bump, often on sun-damaged skin in elderly people.
Credit: DermNet NZ
Merkel cell carcinoma often presents on the head or neck.
Credit: DermNet NZ